Nonstandard Industry Made-to-Order or Plw Plywood Case Chain Sprocket Motorcycle Parts

 Chain Wheel Catalog.pdf
Chain Wheel Catalog.pdf
Introduction to Sprockets
A sprocket is a critical power transmission component in mechanical drive systems. It transmits motion and power through meshing with a chain, and is widely used in various industrial equipment, vehicles, and automated machinery. Below is a detailed introduction to sprockets from multiple dimensions:
I. Basic Definition and Working Principle of Sprockets
Definition
A sprocket is a wheel-shaped mechanical part with evenly distributed teeth. Its tooth profile matches the links of a chain, driving the chain to move through the engagement between teeth and chain links, or transmitting the chain’s motion to other components.
Working Principle
Sprockets and chains form a chain drive system, which belongs to the meshing transmission category. When the driving sprocket rotates, its teeth push the chain links, causing the chain to move with the sprocket. Meanwhile, the driven sprocket is driven to rotate by the chain through meshing, thereby transmitting power from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. Compared with belt drives, chain drives have no slipping and ensure accurate transmission ratios; compared with gear drives, chain drives can achieve transmission with a larger center distance between two shafts.
II. Main Classifications of Sprockets
Sprockets can be classified in various ways, with common criteria including structure, application, and standard specifications:
Classification by Structural Form
Integral sprockets: The tooth part and hub are an integrated structure. They are suitable for small-sized, light-load applications, with simple manufacturing processes and low costs.
Combined sprockets: Composed of a tooth ring and a hub, they are often used in large-sized or heavy-load scenarios. The tooth ring (the wear-prone part) can be replaced independently, reducing maintenance costs.
Split sprockets: Designed with a split structure (e.g., two halves connected by bolts), they allow easy installation or replacement without disassembling the entire shaft, making them convenient for maintenance in tight spaces.
III. Key Parameters of Sprockets
Several core parameters determine a sprocket’s performance and compatibility with chains:
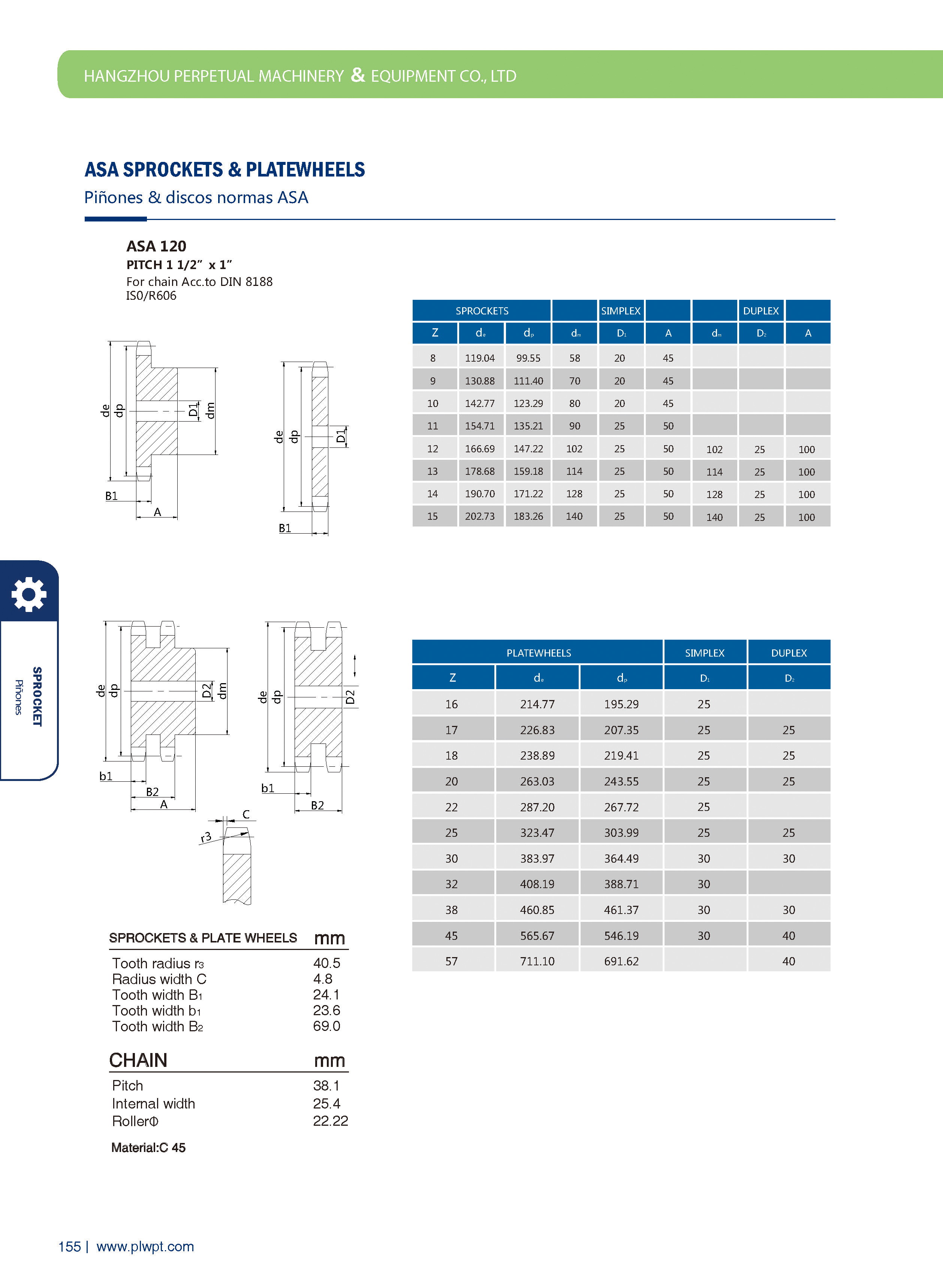
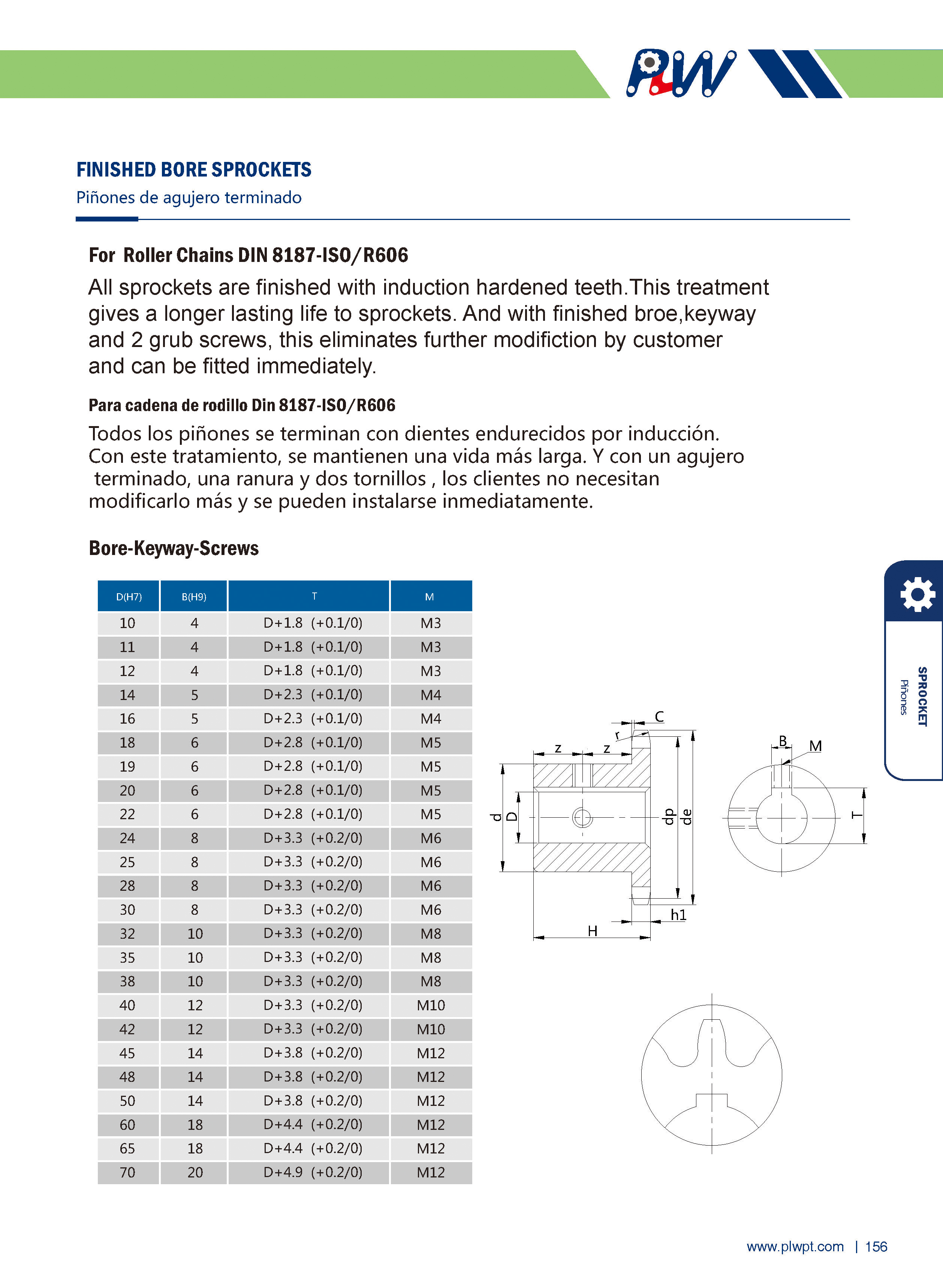
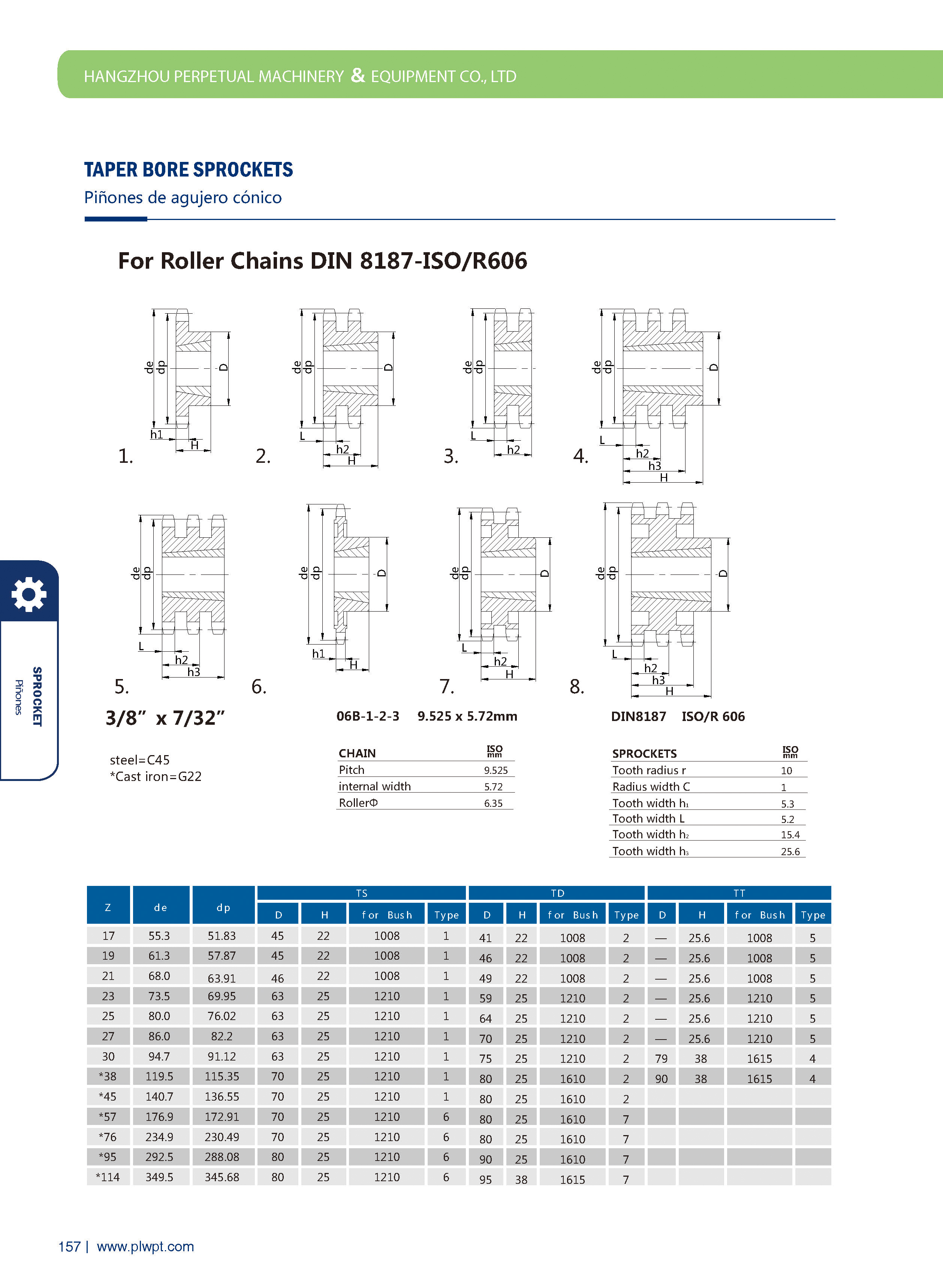
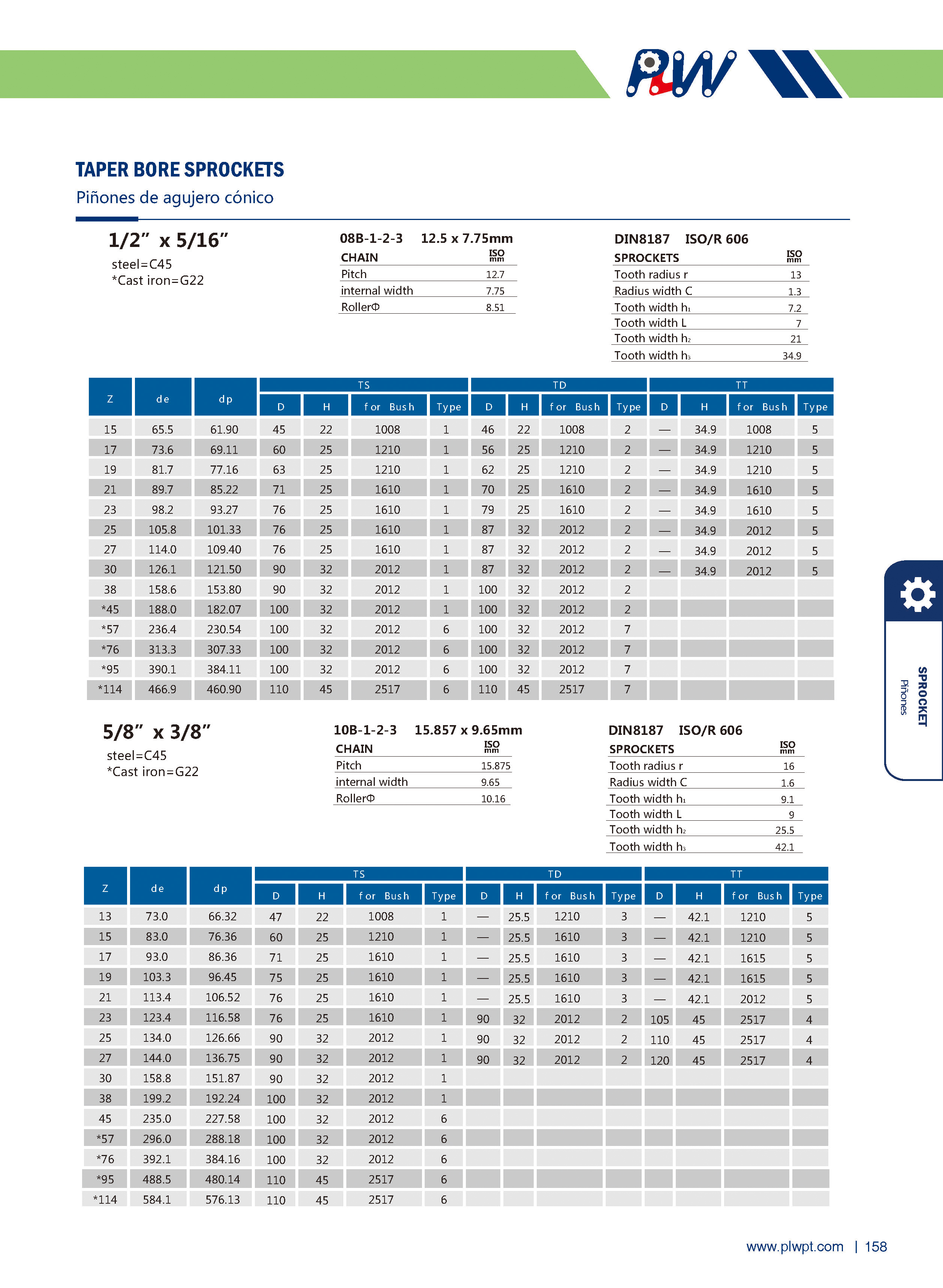
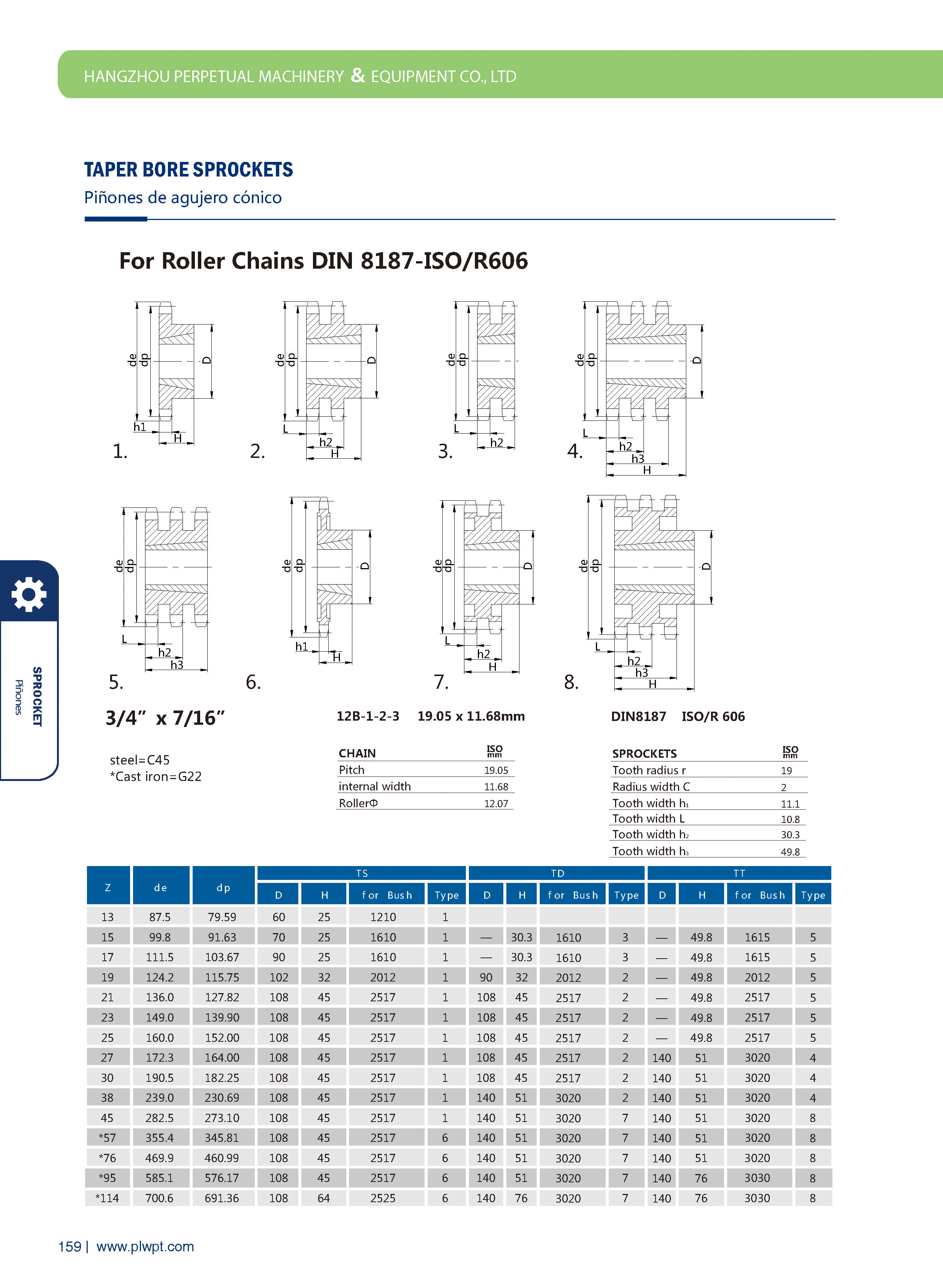
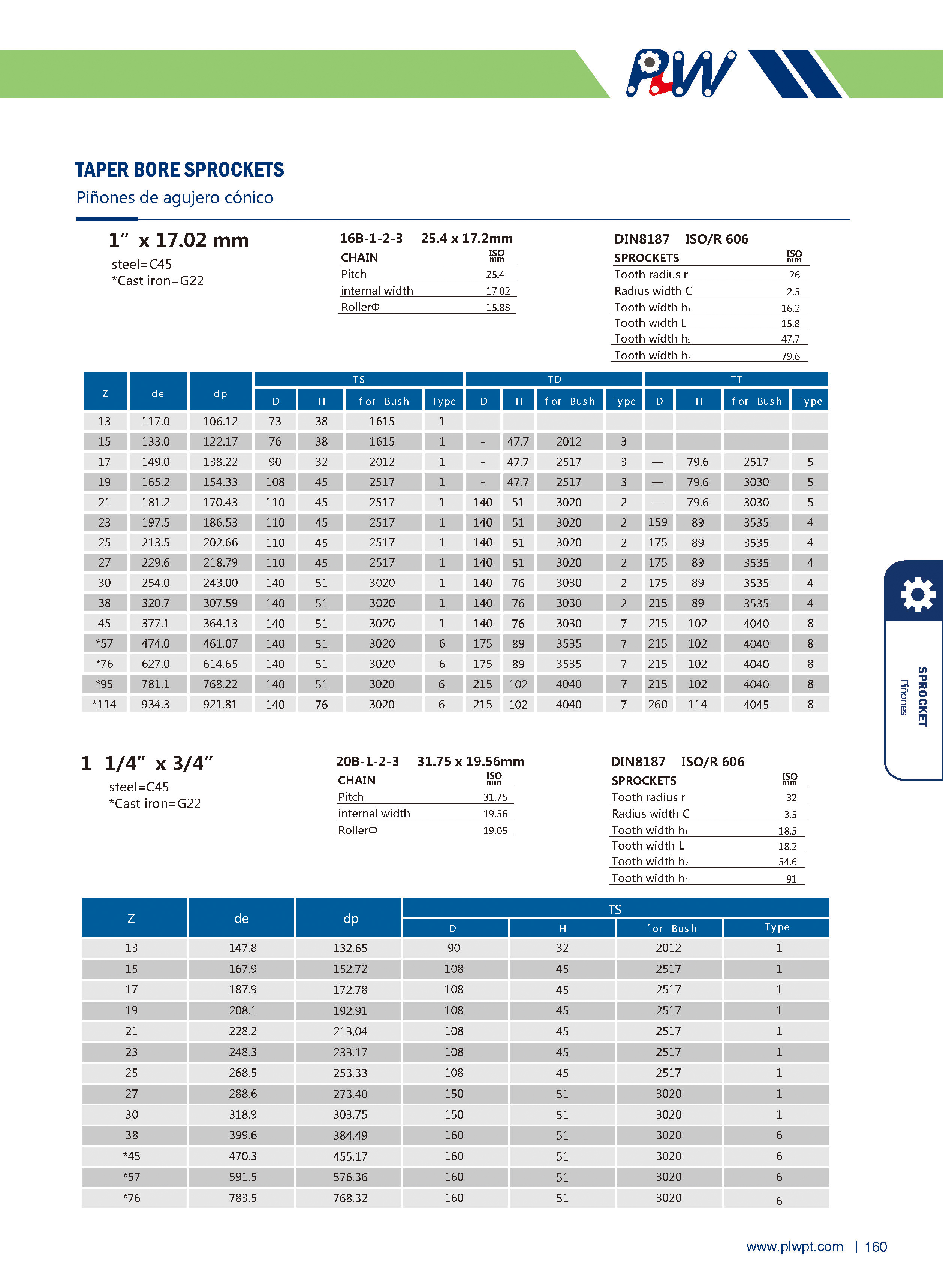
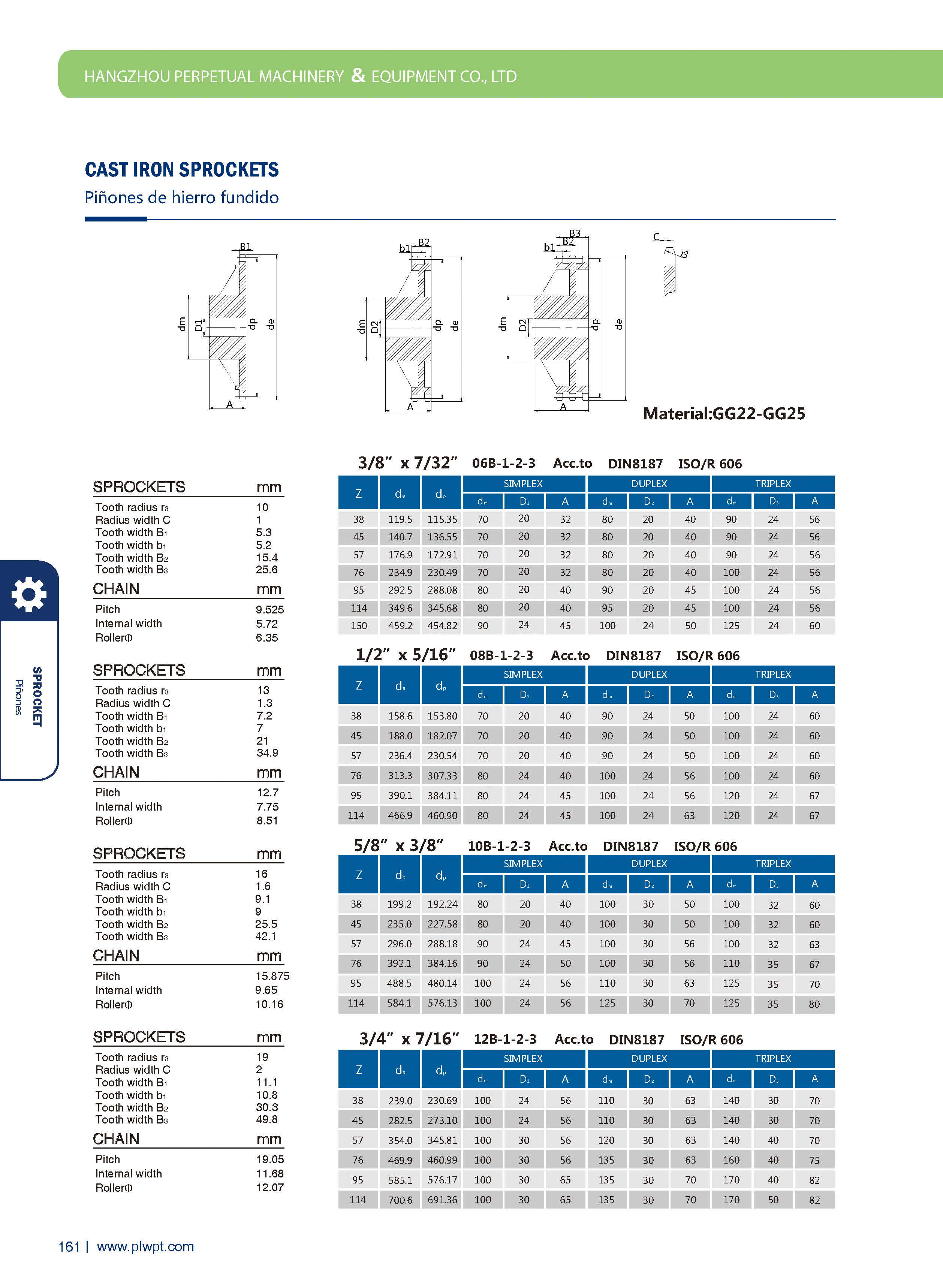
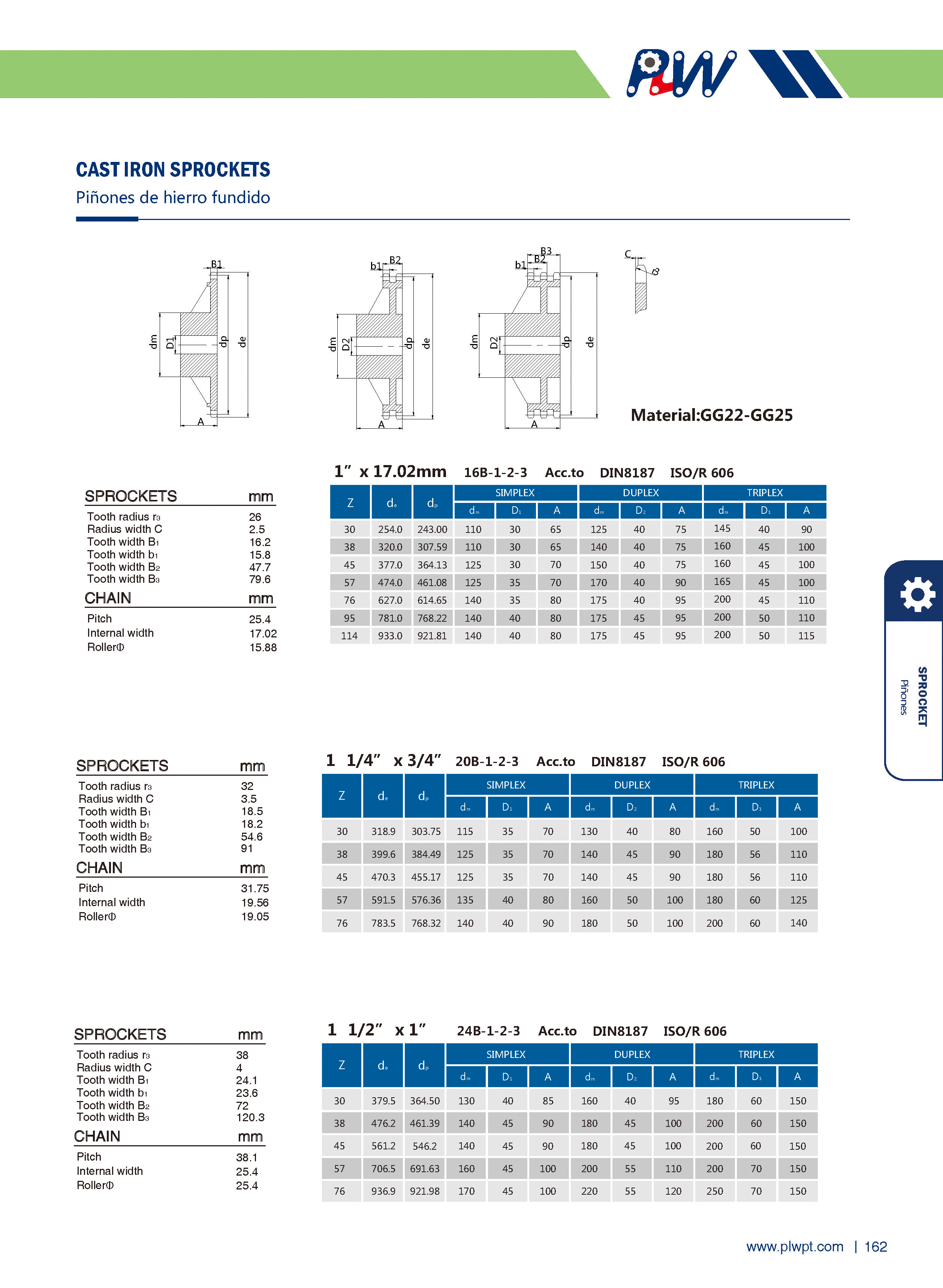
Number of teeth (Z): The total count of teeth on the sprocket. It affects transmission smoothness—more teeth generally reduce vibration, but too many may increase inertia.
Pitch (P): The distance between corresponding points of adjacent teeth (e.g., between the centers of two adjacent tooth grooves). It must match the pitch of the mating chain to ensure proper meshing.
Tip diameter (da): The diameter of the circle passing through the tips of all teeth. It influences the sprocket’s outer size and clearance with surrounding components.
Root diameter (df): The diameter of the circle passing through the bottoms of the tooth grooves. It relates to the sprocket’s strength and the chain’s fit.
Face width (b): The width of the sprocket’s tooth part, matching the chain’s width to ensure stable engagement and prevent lateral slippage.
IV. Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Materials
Sprockets require materials with high wear resistance, strength, and toughness. Common options include:
Carbon steel: Such as 45# steel, often used for medium-load sprockets after quenching and tempering to improve hardness.
Alloy steel: Like 40Cr or 20CrMnTi, suitable for heavy-load or high-speed applications. They may undergo carburizing, quenching, or nitriding to enhance surface hardness and wear resistance.
Cast iron: For low-speed, light-load scenarios (e.g., agricultural machinery) due to its low cost and ease of casting.
Non-metallic materials: Such as nylon or engineering plastics, used in food processing or noise-sensitive environments for their corrosion resistance and low noise.
Manufacturing Processes
Cutting processing: Including hobbing, shaping, or milling to machine the tooth profile, suitable for small-batch production or precision sprockets.
Casting: For large sprockets or complex structures, using sand casting or investment casting to form the rough shape, followed by machining for precision.
Forging: For high-strength sprockets, forging improves material density and mechanical properties before machining the teeth.
Heat treatment: Processes like quenching, tempering, or surface hardening are applied to enhance wear resistance and fatigue strength.
V. Applications of Sprockets
Sprockets are indispensable in numerous industries due to their reliable transmission performance:
Industrial machinery: Used in conveyor systems, printing presses, and textile machinery for stable material or component conveying.
Automotive and transportation: Applied in motorcycle drive chains, bicycle chains, and agricultural vehicle transmissions.
Agriculture: Used in tractors, harvesters, and irrigation equipment to transmit power in harsh working environments.
Construction and mining: Employed in excavators, conveyors, and crushers for heavy-load power transmission.
Food processing: Non-metallic sprockets (e.g., nylon) are used to avoid contamination and reduce noise in food production lines.
VI. Maintenance and Selection Tips
Maintenance
Regular lubrication: Apply chain lubricant to the meshing area of sprockets and chains to reduce friction and wear.
Inspection for wear: Check for tooth wear (e.g., tooth thinning or deformation) and replace sprockets promptly if excessive wear is found to prevent chain slippage or breakage.
Alignment adjustment: Ensure driving and driven sprockets are properly aligned to avoid uneven wear on teeth and chains.
Selection Tips
Match chain specifications: The sprocket’s pitch, tooth number, and face width must match the chain’s parameters (e.g., ANSI, ISO, or GB standards).
Consider load and speed: Choose materials and heat treatment processes based on transmission load (light, medium, or heavy) and rotational speed.
Environmental factors: Select corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., stainless steel or plastics) for humid, corrosive, or food-grade environments.
In summary, sprockets play a vital role in mechanical transmission, and their performance directly affects the efficiency and reliability of the entire system. Proper selection, manufacturing, and maintenance of sprockets are essential for ensuring stable operation in various industrial applications.
English
Español
العربية
Français
Русский
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
සිංහල
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी































